Weighted Average Forecast Method
This forecast method assigns more importance (weight) to the most recent periods. This weight is assigned depending upon the number of historical slices that are to be used in the forecast. This forecast method responds to trends more quickly than a Moving Average forecast, but the result is still a flat forecast with no discernible trend. Weighted Average forecast method requires a minimum of one month of demand history.
In the following example, the weighted average of the first four periods is used to predict the fifth period:
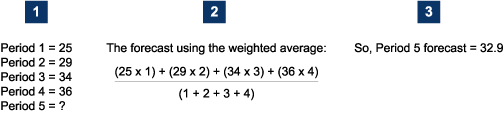
Like the average forecast method, there is an obvious shortcoming with this method. As seen in the above example, the Weighted Average method comes a little closer to a reasonable guess, and increasing the weighting at the end of series would improve the estimate, but using weighted average does not reflect trends accurately.
Each forecast method has constraints, called best fit rules that may make it ineligible for forecasting. |